1.4
Dental malocclusion
Occlusion is the relationship of the teeth in the mandibular arch to those in the maxillary arch as they are brought together. The occlusion is examined and recorded during the oral examination. Patients with malocclusion are usually referred to the orthodontist.
The symptoms of malocclusion may be mild or severe. Typical signs of this disorder include: improper alignment of the teeth, alternation in the appearance of the face, frequent biting of the inner cheeks or tongue, discomfort when chewing or biting, speech problems, breathing through the mouth rather than the nose.
1.4.1
Ideal dentition
The ideal dentition is characterized by an ideal alignment of the upper and lower teeth and by an intermaxillar relationship (between both arches) showing neither anterior-posterior nor transverse discrepancies. It means that all teeth in maxillary arch are in maximum contact with all teeth in mandibular arch in a definite pattern, or maxillary teeth slightly overlap the mandibular teeth on the facial surfaces.
+

Fig. 11. Ideal dentition
1.4.2
Causes of malocclusion
Malocclusion can be an inherited condition. It means it can be passed down from one generation to the next. Besides there are some conditions or habits that may change the shape of the jaw. These can be:
- frequent use of a pacifier after the age of 3
- long usage of bottle feeding in early childhood
- thumb sucking
- injuries that result in the misalignment of the jaw
- abnormally shaped or impacted teeth
- tumours in the oral cavity
- enlarged adenoids or tonsils
1.4.3
Frequent malocclusion
Malocclusion is diagnosed through routine dental examination. X-ray investigation can be done for detection.
According this examination, the facial profile is determined:
Class 1
The upper teeth overlap the lower teeth. The bite is normal and the overlap is slight.
Class 2
We talk about retrognathia. A severe overbite is present. The upper teeth and jaw significantly overlap the lower jaw and teeth.
Class 3
A severe underbite is diagnosed – prognathism. The lower jaw protrudes forward, it means the lower teeth overlap the upper teeth and jaw.
+
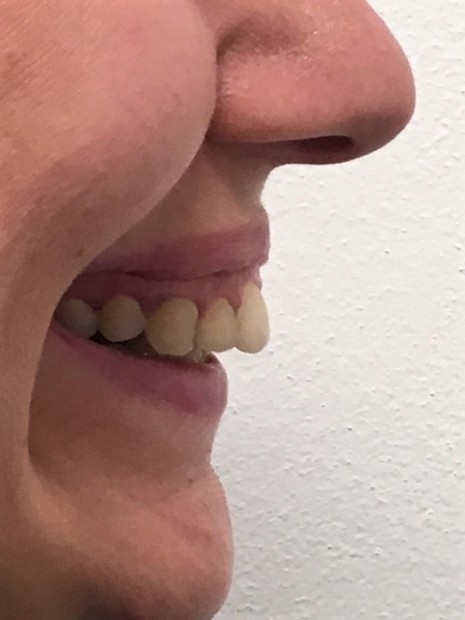
Fig. 12. Retrognathia
According malrelations of groups of teeth we can distinguish:
Cross bites – tooth (teeth) has a more buccal or lingual position than its corresponding tooth in the upper or lower arch. Can be seen in prognathism.
Edge to edge bite – incisal surfaces of maxillary teeth occlude with incisal surfaces of mandibular teeth instead of overlapping as in normal occlusion.
End-to-end bite – molars and premolars occlude cusp-to-cusp.
Open bite – it means lack of occlusal or incisal contact between certain maxillary and mandibular teeth. The teeth cannot be brought together.
Overbite – is the vertical distance by which the maxillary incisors overlap the mandibular incisors.
Most people with mild malocclusion will not require any treatment. If the severe malocclusion is detected, the patient is sent to the orthodontist, who recommends suitable treatment.

Video 2. Causes and types of malocclusion (the user will be directed to an external page)
1.4.4
Treatment of malocclusion
The orthodontist can suggest braces to correct the position of the teeth, or removal of teeth to correct overcrowding, reshaping, bonding of teeth. The jaw can be surgically reshaped or shortened.
Disadvantage
These processes of correction can result in some complications, e. g. tooth decay, pain or discomfort, irritation of the mouth from the use of braces, difficulty chewing or speaking.
Dental hygienist has to interpret the general, functional, and aesthetics purposes of orthodontic care to the patient. She will help with selection of proper toothbrush, applicate tooth brushing method or methods. She will reduce dental plaque or calculus in areas where teeth are crowded or where the braces are in the contact with teeth.
+
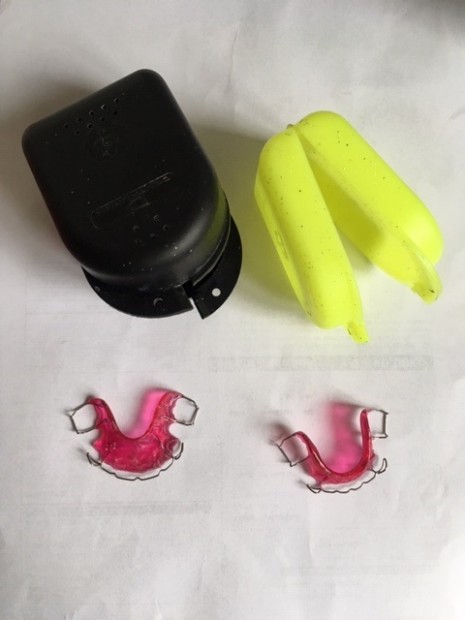

Fig. 13. Braces
Summary
Early detection of malocclusion will help cut down on the length of treatment needed for problem correction.
Vocabulary
English | Czech | English | Czech |
occlusion | skus | malocclusion | chybný skus |
orthodontist | ortodontista | alignment | seřazeni do řady |
alternation | změna | appearance | vzhled |
chewing | žvýkání | biting | kousání |
inherited | dědičný | habit | zvyk |
pacifier | dudlík | thumb sucking | cucání palce |
filling | výplň | adenoids | nosní mandle |
overlap | přesahovat | overbite | překus vertikální |
crossbite | zkřížený skus | edge-to-edge | skus hrana na hranu |
open bite | otevřený skus | bite together | skousnout |
reshaping | tvarování | overcrowding | přeplnění |
bonding | spojení | irritation | podráždění |
©
For licensing reasons, this interactive object cannot be directly incorporated into the material. Click HERE to see the object.
Interactive object 5. Choose the correct word (the user will be directed to an external page)