1.1
Toothbrush
A toothbrush is the basic instrument for removing bacterial plaque. There exist many different designs of toothbrushes. Patients without professional advice concerning the best brush for their oral conditions usually have used brushes selected according to cost, availability, advertising claims, family tradition, or habit. Dental hygienist should know a wide range of available products to advise to patients appropriately.
1.1.1
Early toothbrushes
First notices can be found in the Chinese literature to about 1600 BC.
Later, many preparations used as dentifrices and mouthwashes were developed. During the 18th century, there were mentioned toothbrushes made of horse´s hair but they were destructive to the teeth. By the early 19th century handles of gold, ivory, or ebony in which replaceable brush head could be fitted were constructed. Around the 1900, celluloid was available for toothbrush handles. Toothbrush bristles were generally made of Siberian hog hair.
Since World War II synthetic materials have been improved. Nearly all current toothbrushes are made of synthetic materials. Powered toothbrushes have been used since 1960.
Characteristics of an effective toothbrush
- suits to patient requirements in size, shape, and texture
- is easily and efficiently manipulated
- is easily cleaned and impervious to moisture
- is flexible
- has end rounded filaments or bristles
1.1.2
Parts of toothbrush
+

Fig. 1. Parts of a toothbrush
- Handle – the part grasped in the hand during brushing
Nearly all handles are plastics. It allows durability, imperviousness to moisture, low cost, rigidity, and smooth texture. It should be easy to grasp, shouldn´t slip or rotate in hand. For patient with disability it can be bent or thickened.
- Shank – the part between the head and the handle
Some types can be angled without heating.
- Head – the working part. It consists of tufts of bristles or filaments.
Tufts are individual bundles of filaments secured in a hole of the toothbrush head. It should be large enough to accommodate the tufts but small enough to reach every piece of patient´s mouth, areas such as extension onto proximal surfaces, malpositioned teeth. All the filaments should be soft and end rounded. Most current toothbrushes have nylon filaments and a variety of filaments profiles are available.
Profiles can be flat (all filaments are the same length), rippled (tufts are angled in different position), Bi-level (there are two levels of filaments), Bi-level orthodontic (various bi-level shape). According to the stiffness of filaments we distinguish extra soft, soft, medium, or hard brushes.
Ability of the patient to use the toothbrush, position of teeth (crowded or spaces), personal preferences and recommended brushing method are influencing factors in a toothbrush selection.
1.1.3
Care of toothbrushes
The human body is every day exposed to harmful bacteria and microbes. If the person is in a good condition his/ her body is able to defend himself/ herself against infection. The patient should low the risk of infection with proper care of toothbrush.
There are some tips how to clean toothbrush.
- Rinse toothbrush with clean water after each brushing to remove any toothpaste and debris, and bacteria between the filaments. Put toothbrush under strong stream of warm water.
- Store the toothbrush in an upright position.
- Let the toothbrush to air dry.
- The toothbrush should be separated from the others even if they are kept in one holder.
- Use cover or closed containers only for use at work, school, or travel. Portable container should have sufficient holes to give air.
- Do not share your toothbrush. Body fluids and microorganisms could be shared between the users.
- Replace toothbrush every three months. The bristles or filaments become frayed, splayed and worn. Cleaning effectiveness will decrease. The period depends on patient´s technique and quality of filaments. Also rougher brushers should replace their toothbrushes more frequently.
- When a patient experiences an infectious disease, he should replace the brush as well.
+
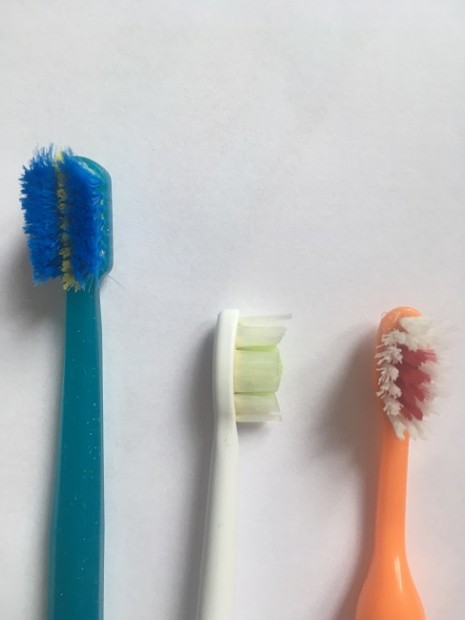

Fig. 2. Worn out toothbrushes
1.1.4
Kinds of toothbrushes
1.1.4.1
Manual toothbrush
We can choose from a wide range of toothbrushes.
There is a type with a conventional head shaped like a rectangle with rounded corners, or a diamond head, which is narrower at the top to reach tight spaces around the back teeth.
Types according to the hardness of the bristles. Extra soft, soft _ bristled toothbrush is recommended for sensitive teeth and gums, or for patients after surgery in the oral cavity. If you have troubles with plaque building up, you should use a medium bristles for effective cleaning. Hard bristled toothbrush is designed for dentures.
Next kind is according bristle pattern. Flat bristles are effective at cleaning front teeth, but sometimes it could be difficult to reach back teeth. Rippled pattern is said to remove plaque better than some other patterns. Bi-level orthodontics are usually used by patients with braces.
First toothbrush
Between the sixth and tenth month we can see the baby´s first tooth starts to poke through tiny gums. It is fine to start with care as soon as possible.
A baby gum brush – cleans an infant ´s gums before the first tooth grows up. It usually fits on finger like a thimble, or we wrap it around our finger. It is used without toothpaste.
A teether toothbrush – is a nubby teether and in addition it relieves gum pain. It´s used without toothpaste.
The first baby toothbrush – is a tiny brush with soft bristles and rubber covered head. We start to use toothpaste of pea sized amount.
A toddler toothbrush – is created for independency of children to hold and brush their teeth. They have large handle and small head to fit perfectly in the small oral cavities of children. Adults should still supervise brushing and complete brushing after child´s brushing.
A child toothbrush – is a toothbrush with thinner handle compared to toddlers. These toothbrushes are usually with superhero or cartoon characters drawn on them. Children are more interested in brushing then.
+
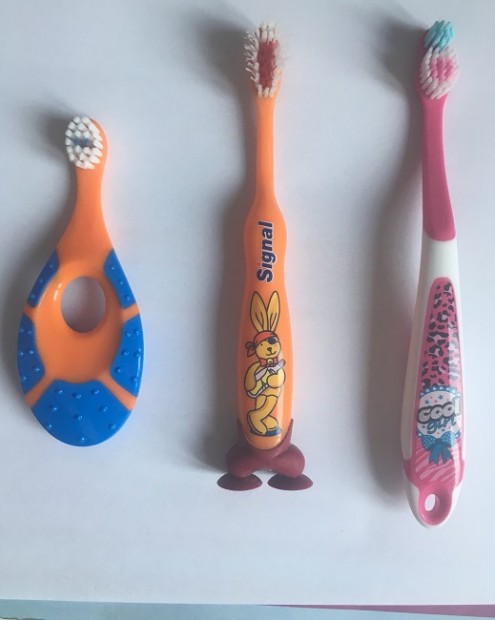

Fig. 3. First toothbrushes
1.1.4.2
Electric toothbrush
These toothbrushes are known as mechanical, electrical, or sonic toothbrushes. Comparisons have been made between the electrical and the manual brushes to determine the ability to remove plaque and prevent calculus development. Both types have been shown effective when used correctly.
Electric toothbrushes can be classified according to the speed of their movements as power, sonic and ultrasonic toothbrushes.
- Electric toothbrush acts vibration or rotation-oscillation movement (a brushing technique like with a manual toothbrush or you brush your teeth one after another).
- Sonic toothbrush has movement which is fast enough to produce vibration in the audible range.
- Ultrasonic toothbrush acts ultrasonic waves, which break up bacterial chains that make up dental plaque.
We have to take care of the brush head as well as in case of manual toothbrush. It is recommended to change it every three to six months, or when it is visibly deteriorated.
We have to have also power source. In older models (not used in these days) we found a battery, not always replaceable, fitted in the handle. With new environmental laws, contactless inductive charging is preferred. We easily place our toothbrush into glass holder/ charging stand and it starts charging.
There exist some pleasant functions and accessories. Many modern electric toothbrushes have a timer which buzzes, plays melodies, or briefly interrupts power usually after 30 seconds. It is a signal for you to change quadrant of the mouth. After 2 minutes the process is completed. The toothbrush rings, lights up or the handle vibrates and alerts the user the end of the cleaning. It can be shown on LCD screen and all your data can be transmitted from your toothbrush to your smartphone, or other device. There is not only the information about the length of brushing but also if you applied too much pressure, or skip some places. In really up to date toothbrushes the application can turn to send data back to the toothbrush and change the cleaning modes, and cleaning time. It helps to improve brushing technique and habits. May be one negative can be mentioned. You have to write down your personal data to use this application.
You can store the head hygienically in handy glass case. If you travel, you use travel case with USB charged travel case.
+
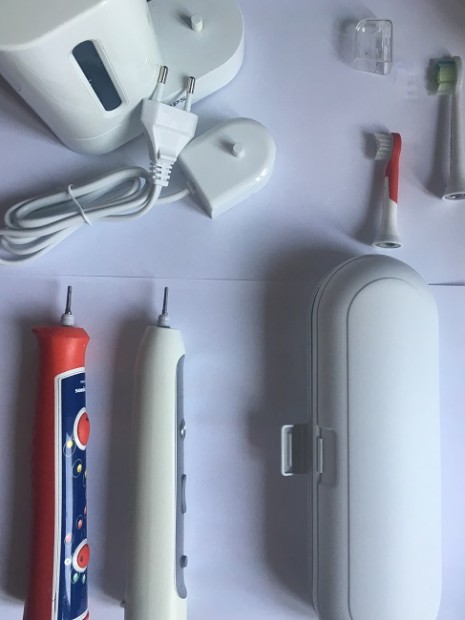

Fig. 4. Sonic toothbrushes
Vocabulary
English | Czech | English | Czech |
design (for) | určit (pro) | Claim | tvrzení |
mouthwash | ústní voda | Dentifrices | zubní pasty |
Handle | držadlo | Ivory | slonovina |
Ebony | eben | Celluloid | celuloid |
bristles | štětiny | Siberian hog | divoké prase |
current | současný | powered | elektrický |
effective | účinný | Requirement | požadavek |
Shape | tvar | texture | struktura |
imperviousness | nepropustnost | moisture | vlhkost |
filament | vlákno | grasp | uchopení |
durability | trvanlivost | rigidity | tuhost |
Angled | zahnutý | tuft | svazeček |
Bundle | svazek | extension | natažení |
malposition | špatné postavení | nylon | nylon |
Flat | plochý | rippled | zvlněný |
stiffness | tvrdost | harmful | škodlivý |
Defend | bránit | rinse | vypláchnout |
Debris | zbytky jídla | cover | víčko |
Frayed | roztřepené | splayed | sešikmené |
rectangle head | obdélníková hlava | diamond head | zužující se hlava |
Narrow | úzký | poke | prorazit |
toddler | batole | relieve | ulevit |
Nubby | hrbolatý | instrument | nástroj |
availability | dostupnost |
©
For licensing reasons, this interactive object cannot be directly incorporated into the material. Click HERE to see the object.
Match the correct words (the user will be redirected to an external page)
1.1.5
Compliments to toothbrush
1.1.5.1
Single end brush
It is a compliment of regular toothbrush. It is capable of cleaning crowded teeth, molars, areas between braces, dentures, bridges, implants, etc. Teeth that are positioned next to gaps are cleaned better with this brush as well as the gum lines. The designs of the single toothbrushes vary, some of them have wider handle, straight shank or angled shank and shape of the tufts also differ.
+
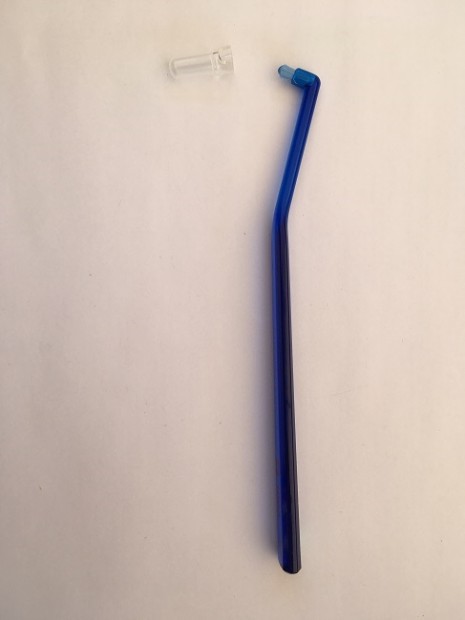

Fig. 5. Single end brush
1.1.5.2
Interdental toothbrush
It is always a compliment to toothbrush. It reaches the spaces that are normally inaccessible by toothbrush. It should be used after brushing. It cleans the places between our teeth. If the patient wears braces it can also be used to clean the areas between the wires and teeth.
+
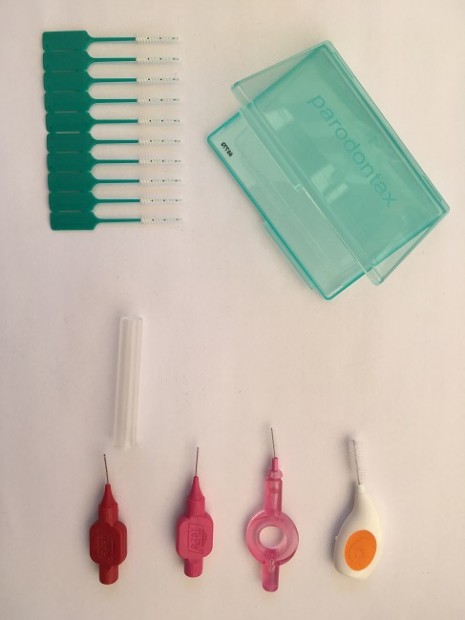
Fig. 6. Interdental toothbrush
These toothbrushes exist in different sizes and colour codes. A dental hygienist determines correct size with colour coding probe. It can happen that a patient uses two or three different sizes, (more is likely to be counterproductive). Their heads can either be straight or angled (better for areas in back). We can use a holder for interdental toothbrush, angled or straight. The angled holders make it easier to clean the side teeth. If you are travelling, you can keep it in a pocket set.
+
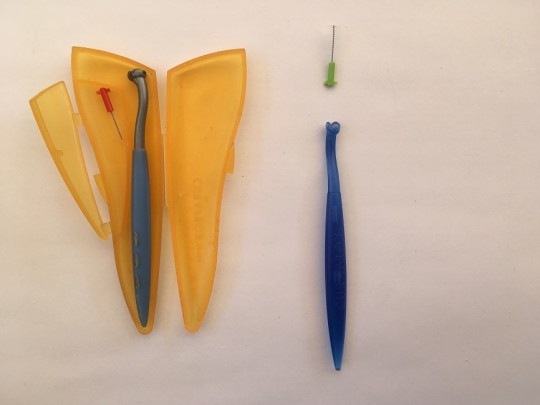

Fig. 7. Interdental toothbrush pocket set
1.1.6
Dental floss
The front teeth are often very close together. Sometimes they are so tight that interdental toothbrush cannot be used. Then we can use dental floss. It is good for implant care as well. We should floss once per day before brushing. We clean spaces between teeth and allow the fluoride from the toothpaste to reach them. Floss is made of nylon multifilaments or PTFE (plastic monofilament polytetrafluoroethylene). It can be waxed or unwaxed, in circular form (floss) or flat form (tape). Another types of floss are made from either natural, biodegradable silk, or natural floss infused with charcoal, or floss from bamboo. The handle can be made from corn starch – this floss is completely biodegradable.
People often prefers interdental toothbrushes because flossing is not easy process and they cannot do it effectively and very often can cut into the gum and cause bleeding. Common causes of floss cuts are either using too long piece of floss between the fingers when held for insertion, or snapping the floss through the contact area, or not curving the floss about the teeth.
1.1.6.1
Aid for flossing
Floss pick - several types of floss holders are available. Handle is designed with two prongs in Y or F shape. They are very helpful for people with disability or caregiver serving child or patient. It is easy to use when travelling.
+
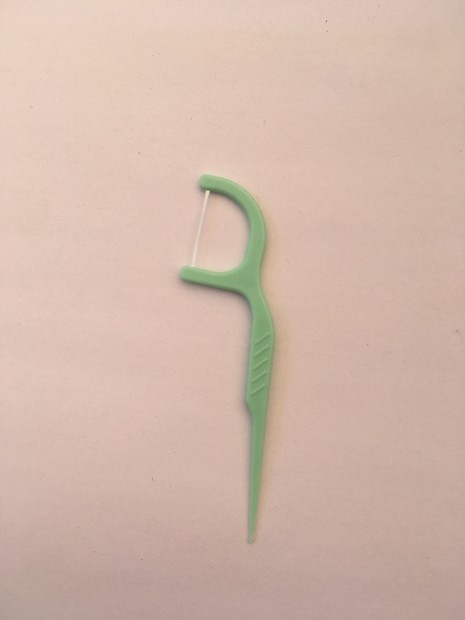
Fig. 8. Floss pick
Powered floss pick - this is not an electrical floss. It has no batteries because this floss is powered by air. We have to fill it with water or mouthwash. The air infusion technology blasts away all left particles.
Toothpick – is a small stick made of nylon, plastic or other synthetic material. It can be flexible or rigid. It has simple or flocked tip. Of course eco-friendly materials are available, e. g. toothpick made of natural bamboo, which has polished and smooth surface. Completely natural toothpicks are curry leaf stem, tea tree stem, or lemon tree stem.
They are not recommended by dentists, because interdental toothbrush and floss are much safer.
1.1.7
Mouthwash
There are two basic kinds of mouthwash. The essential oils and chlorhexidine one. They are used for lowering of plaque and gingivitis occurrence.
Dental hygienist should show to the patient, mainly children, how to rinse. (Take a small amount of the fluid into the mouth. Close lips. Force the fluid through the interdental areas with pressure. Balloon the cheeks, then suck them, several times, and expectorate.)
Commercially sold products can contain eucalyptol, menthol, thymol, and methyl salicylate (e. g. Listerine), or CPC (cetyl pyridinium chloride) (e. g. Colgate Plax, Oral B Pro Health Rinse).
The therapeutic product is e. g. Chlorhexidine. It is one of the most effective antiplaque and anti-gingivitis chemotherapeutic agents. It lowers the oral bacterial count. It can only be used for a short time, two weeks max., because of its side effects. It can leave brown stains on the teeth or tongue. Patient can feel burning sensations of the mucosa, lose taste temporarily etc.
©
For licensing reasons, this interactive object cannot be directly incorporated into the material. Click HERE to see the object.
Language game (the user will be redirected to an external page)